Many of our add-in products require that you have Visual Basic for Application (VBA) installed as part of your Microsoft Office installation.
In addition to being installed, it must be enabled.
Both of the above may be set by the administrator(s) of your computer.
We explain below how to check.
Is VBA Installed for PowerPoint, Excel and Word?
Follow either of these methods to establish if VBA is installed:
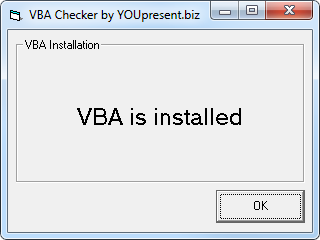
Method 1 : Run our simple VBA Checker application in Windows
- Download and run our VBA Checker app which queries Microsoft Word to get an instant status:
Method 2 : Open the Visual Basic Editor (VBE)
- Open PowerPoint, Excel or Word
- Press Alt+F8 on your keyboard
- If a new VBE window opens, VBA is installed and enabled
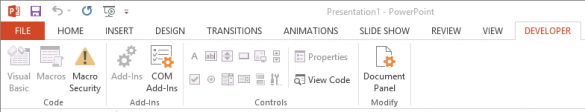
Method 3 : Enable and Check the Developer Ribbon
- For Office 2013, open PowerPoint, Excel or Word and click File
- Click Options
- Click Customize Ribbon
- Check the box next to Developer in the right hand side of the window
- Click OK
- If the Developer tab has either of the Visual Basic or Add-Ins buttons greyed out, then VBA is not available:
Method 4 : Windows Control Panel (only if you’re not using Office 365)
- Open the Windows Control Panel
- Click Programs and then Programs and Features
- Find the Microsoft Office program
- Click Change
- Follow the instructions to get to Custom Settings
- Locate the Visual Basic for Application item and check to see if it’s installed
Is VBA Enabled?
VBA may be installed but disabled. The simplest check for this is to run any Office Application and press Alt+F11. If the VBE (Visual Basic Editor) doesn’t open, it may be that VBA is disabled. The definitive method to check this is to look at the Windows Registry but note, making any changes to the registry can cause problems with your PC. You will also need administrator rights to run regedit.exe
- Start the Registry Editor (In Windows 10, type regedit in the taskbar search box. In Windows 8 : go to the Start screen and type regedit. In Windows 7 : click Start and type regedit)
- For standalone installations, locate the following keys, where XX is the version of Office installed (16.0 = 2016, 15.0 = 2013, 14.0 = 2010, 12.0 = 2007, 11.0 = 2003)
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Office\XX\Common\VBAOff
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\XX\Common\VBAOff - For corporate installations, System Policy may be have been used to disable VBA and the key is found here:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Office\XX\Common\VBAOff
For further information, refer to this Microsoft article: How to turn off Visual Basic for Applications when you deploy Office